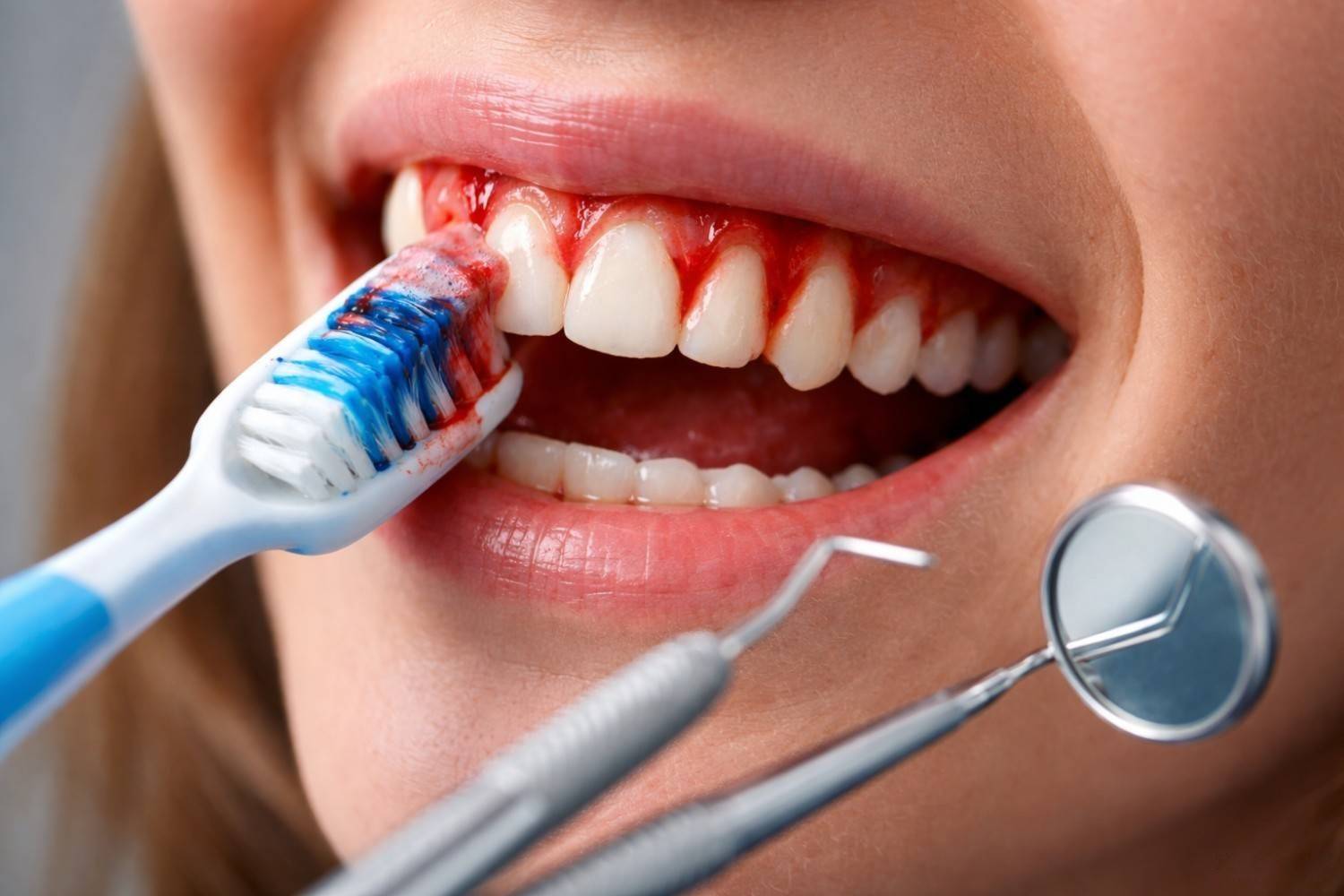
If your gums bleed while brushing or flossing, you’re not alone but that doesn’t mean it’s normal. Occasional gum bleeding may result from brushing too hard or starting a new flossing routine. However, persistent bleeding gums are often a sign of an underlying issue that requires attention. If bleeding from gums lasts more than one to two weeks or comes with other symptoms like swelling, pain, or bad breath, it should not be ignored. Early intervention can prevent minor irritation from turning into serious gum disease.
This guide will walk you through the common and serious causes of bleeding gums, clarify when it’s a harmless occurrence versus a red flag, outline effective treatments, and help you understand exactly when it’s time to consult a dental professional.
Common Causes of Bleeding Gums
Several factors can lead to gum bleeding, ranging from poor oral hygiene to systemic health conditions.
- Plaque and tartar buildup: The most common cause. Plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, irritates the gums, leading to inflammation and bleeding while brushing.
- Gingivitis: This early stage of gum disease occurs when plaque isn’t removed, causing red, swollen, and bleeding gums.
- Aggressive brushing or flossing: Using a hard-bristled toothbrush or applying too much pressure can damage delicate gum tissue.
- Vitamin deficiencies: Low levels of vitamin C or K can impair gum health and increase susceptibility to bleeding from gums.
- Hormonal changes: During pregnancy, hormonal shifts make gums more sensitive and prone to gum bleeding.
- Medications: Blood thinners may cause increased gum bleeding.
- Systemic conditions: Uncontrolled diabetes weakens the body’s ability to fight infection, making gums more vulnerable.
While some causes are temporary, others signal deeper oral health concerns.
When Are Bleeding Gums Considered Normal?
Not all instances of bleeding while brushing or bleeding when flossing are alarming. Mild gum bleeding can be normal in specific situations:
- When you first start flossing regularly, your gums may bleed for a few days as they adjust.
- Temporary irritation from food particles usually resolves within 2–3 days with proper cleaning.
However, if bleeding persists beyond a week despite gentle oral care, it’s no longer “normal.”
Warning Signs: When Bleeding Gums Are a Serious Concern
Persistent or severe symptoms indicate that bleeding gums may signal infection or advancing gum disease. Watch for these warning signs:
- Bleeding lasts more than 1–2 weeks
- Gums are swollen, red, tender, or painful
- Bleeding occurs without any brushing or flossing
- Teeth feel loose
- Gums appear receding
- Persistent bad breath or metallic taste
These are classic gum disease symptoms often linked to gingivitis progressing toward periodontitis.
| Cause of Gum Bleeding | Key Signs & Symptoms | Typical Duration |
| New flossing routine | Mild bleeding only when flossing, no pain | Resolves in 3–5 days |
| Aggressive brushing | Bleeding at gumline, possible recession | Stops with technique change |
| Plaque buildup | Red, puffy gums; bleeding while brushing | Persists without treatment |
| Tartar accumulation | Hard deposits near gumline; chronic inflammation | Requires professional cleaning |
| Vitamin deficiency | Fatigue, easy bruising, slow healing | Improves with diet |
| Pregnancy | Increased sensitivity, swelling | Often resolves postpartum |
| Diabetes | Slow healing, frequent infections | Needs medical management |
This table helps distinguish temporary irritation from conditions needing professional care.
When to See a Dentist for Bleeding Gums
You should consider seeing a dentist if:
- Gum bleeding persists despite good oral hygiene
- You experience pain, swelling, or fever
- There’s visible pus indicating infection
- Your gums aren’t healing after two weeks
- You suspect links to medication, stress, or systemic illness
Professional evaluation is essential because recurring bleeding gums often require clinical intervention. A dentist can determine whether your symptoms stem from early gum disease or another factor.
Common dental treatments include:
- Professional cleaning to remove plaque and tartar
- Scaling and root planing for deeper infection
- Guidance on proper brushing and flossing
Early visits lead to simpler, less invasive care.
Why Ignoring Bleeding Gums Can Be Dangerous
Ignoring bleeding gums can have serious consequences. Reversible gingivitis can advance to periodontitis, where infection destroys gum tissue and jawbone. This increases the risk of:
- Permanent gum recession
- Tooth mobility and loss
- Complex, costly treatments later
Timely care protects both your smile and overall health.
How Dentists Treat Bleeding Gums
Effective treatment depends on the cause:
- Professional cleaning: Removes buildup that home care misses
- Improved technique: Soft-bristled brush, gentle flossing
- Gum therapy: For diagnosed gingivitis or periodontitis
- Regular check-ups: Prevent recurrence
In cases tied to nutrition or medical issues, coordinated care ensures full recovery.
How to Prevent Bleeding Gums Naturally
Prevention requires consistency:
- Brush gently twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- Floss every day
- Visit your dentist every six months
- Eat foods rich in vitamins C and K
- Avoid tobacco
These habits reduce the risk of plaque-related gum bleeding.
When Bleeding Gums Require Emergency Dental Care
Seek urgent care if you experience:
- Heavy or uncontrolled bleeding from gums
- Severe pain or rapid swelling
- Fever with gum symptoms
- Pus discharge
These suggest acute infection requiring prompt attention.
Conclusion: Take Bleeding Gums Seriously
Recurring bleeding gums should never be dismissed. While occasional spotting may be harmless, persistent gum bleeding is your body’s warning sign whether from poor hygiene, early gum disease, or an underlying health issue. Recognizing symptoms like swelling, bad breath, or bleeding while brushing can help you act before irreversible damage occurs. Prevention, early diagnosis, and professional treatment are the best defenses for long-term oral health.
If your gums bleed frequently or you’re unsure whether it’s serious, a dental check-up can identify the cause early and prevent complications. At Sasane Dental Clinic in Panvel, our team offers expert evaluation and personalized care for bleeding gums and related gum conditions. With convenient locations in both Old and New Panvel, the clinic provides advanced, gentle treatments in a trusted setting. Don’t wait to schedule your appointment today.
FAQs About Bleeding Gums
Are bleeding gums normal?
Occasional bleeding from starting flossing or brushing too hard can happen, but persistent bleeding is not normal and often signals an underlying issue.
What are the most common causes of bleeding gums?
The most common causes include plaque buildup, gingivitis, aggressive brushing or flossing, tartar accumulation, vitamin C or K deficiency, hormonal changes during pregnancy, and certain medications like blood thinners.
When should I worry about bleeding gums?
You should worry if bleeding lasts more than 1–2 weeks, occurs without brushing, or is accompanied by redness, swelling, pain, bad breath, receding gums, or loose teeth.
How long should bleeding gums last?
Bleeding from minor irritation should stop within a few days; if it continues beyond 7–10 days despite good oral hygiene, it’s time to see a dentist.
Do bleeding gums always mean gum disease?
Not always while gum disease like gingivitis is a frequent cause, bleeding can also result from temporary irritation, vitamin deficiencies, or medication side effects.
Can bleeding gums heal on their own?
Mild cases due to new flossing or minor trauma may resolve with improved oral care, but persistent bleeding usually requires professional evaluation and treatment.
When should I see a dentist for bleeding gums?
See a dentist if bleeding is frequent, doesn’t improve in 1–2 weeks, is painful, or comes with swelling, pus, bad breath, or other concerning symptoms.
Can vitamin deficiency cause bleeding gums?
Yes, deficiencies in vitamin C (scurvy) or vitamin K can weaken gum tissue and lead to easy bleeding and poor healing.
Does bleeding gums mean I will lose my teeth?
Not necessarily early-stage bleeding from gingivitis is reversible with proper care, but untreated gum disease can progress to periodontitis, which may eventually lead to tooth loss.
How are bleeding gums treated by a dentist?
A dentist treats bleeding gums by removing plaque and tartar through professional cleaning, performing scaling and root planing if gum disease is present, and providing personalized guidance on oral hygiene and prevention.




